Learn
Endocannabinoid System
Learn how your body is naturally equipped to utilize the cannabis plant’s therapeutic benefits. The human ECS regulates various cardiovascular, nervous, and immune system functions inside cells.
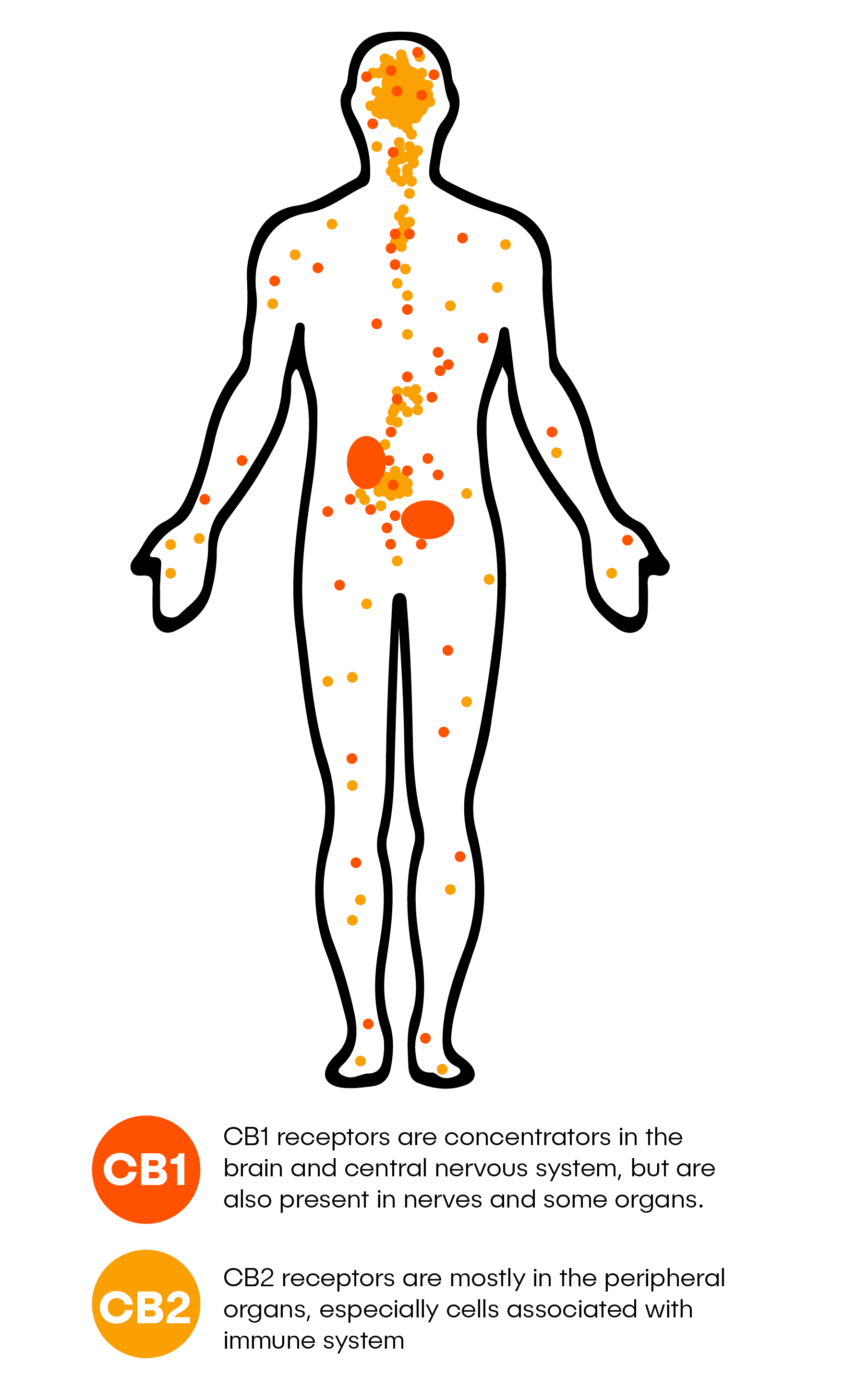
The Human Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a biological system found in all mammals, and is involved in managing a wide variety of biological processes, including memory, sleep, immune response, and more.
It mainly consists of two types of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2).These receptors are built to interact with endocannabinoids (cannabinoids naturally produced by the brain). They can also interact with plant-derived cannabinoids, which in turn cause a variety of responses throughout the body.
Cannabinoids have demonstrated potential for a wide spectrum of therapeutic uses, including: antioxidant, neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory , anti-pain, anti-tumor, sleep modulating effects, anti-psychotic and anti-anxiety.
The most well-known delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is responsible for the “high” of cannabis and can affect perception, mood, emotion, cognition, and motor function. There are also numerous cannabinoids, like cannabidiol (CBD), which are non-psychoactive yet have medically useful properties.
