Learn
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds secreted by cannabis flowers that interact with receptors in the brain to provide relief to an array of symptoms including pain, nausea, anxiety, and inflammation.
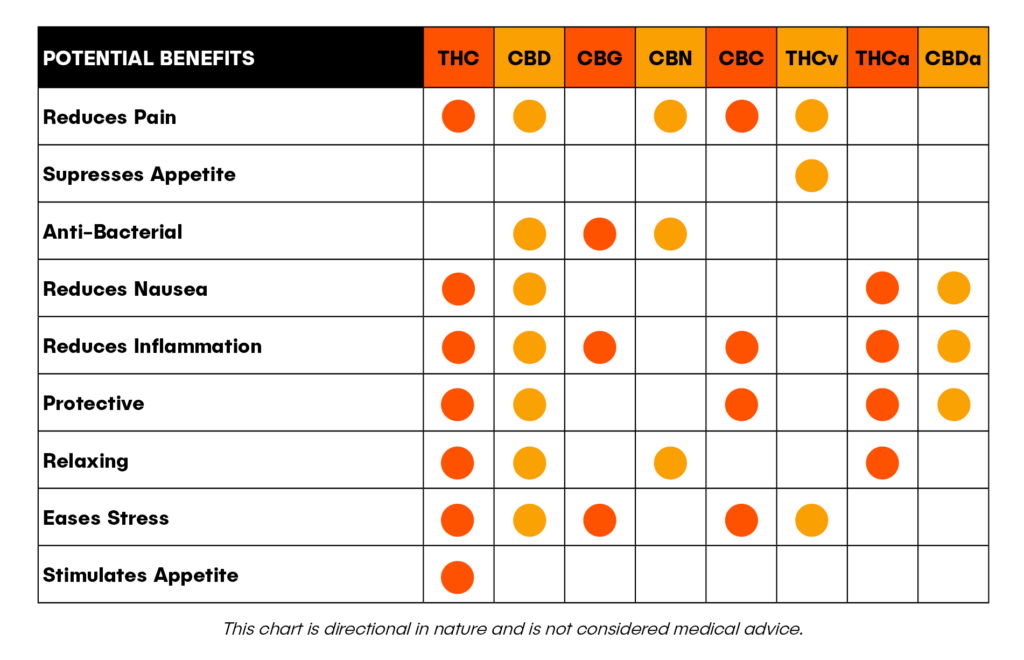
Although all cannabinoids play an important role in providing relief for qualifying conditions and symptoms, the two most popular cannabinoids are THC and CBD.
When cannabis is consumed, cannabinoids bind to receptor sites throughout our brain (receptors called CB-1) and body (CB-2). Different cannabinoids have different effects depending on which receptors they bind to.
For example, THC binds with the CB1 receptors in the brain, which are found mainly in our central nervous system. Their activation has cerebral and behavioral effects which also produces a high or sense of euphoria.
CBD binds with the CB2 receptors, mostly in the peripheral nervous system and associated with the immune system and inflammation response. Activating the CB2 can relax the body, help it repair itself and reduce the sensation of pain without impairing cognition.
Our pharmacists are highly knowledgeable in cannabinoid effects and can help guide you to the right cannabinoid profile for your needs.